主要统计指标解释
能源生产总量 指一定时期内全国(地区)一次能源生产量的总和,是观察全国(地区)能源生产水平、规模、构成和发展速度的总量指标。一次能源生产量包括原煤、原油、天然气、水电、核能及其他动力能(如风能、地热能等)发电量。不包括低热值燃料生产量、生物质能、太阳能等的利用和由一次能源加工转换而成的二次能源产量。
能源消费总量 指一定时期内全国(地区)生产和生活消费的各种能源的总和,是观察能源消费水平、构成和增长速度的总量指标,能源消费总量包括原煤和原油及其制品、天然气、电力。不包括低热值燃料、生物质能和太阳能等的利用 。能源消费总量分为三部分,即终端能源消费量、能源加工转换损失量和损失量。 (1)终端能源消费量 指一定时期内全国(地区)生产和生活消费的各种能源在扣除了用于加工转换二次能源消费量和损失量以后的数量。 (2)能源加工转换损失量 指一定时期内全国(地区)投入加工转换的各种能源数量之和与产出各种能源产品之和的差额。它是观察能源在加工转换过程中损失量变化的指标。 (3)能源损失量 指一定时期内能源在输送、分配、储存过程中发生的损失和由客观原因造成的各种损失量。不包括各种气体能源放空、放散量。
能源生产弹性系数 是研究能源生产增长速度与国民经济增长速度之间关系的指标。计算公式:

国民经济增长速度,可根据不同的目的或需要,用国民生产总值,国内生产总值等指标来计算,本资料是采用国内生产总值指标计算的。
电力生产弹性系数 是研究电力生产增长速度与国民经济增长速度之间关系的指标。一般来说,电力的发展应当快于国民经济的发展,也就是说电力应超前发展。计算公式:

能源消费弹性系数 是反映能源消费增长速度与国民经济增长速度之间比例关系的指标。计算公式:

电力消费弹性系数 是反映电力消费增长速度与国民经济增长速度之间比例关系的指标。计算公式:

能源加工转换效率 指一定时期内能源经过加工、转换后,产出的各种能源产品的数量与同期内投入加工转换的各种能源数量的比率。它是观察能源加工转换装置和生产工艺先进与落后、管理水平高低等的重要指标。计算公式:

土地资源 土地指陆地的表层部分,它主要由岩石、岩石的风化物和土壤构成。土地资源按利用类型可以分为农用地、建筑用地和未利用地。农用地包括耕地、园地、林地、牧草地和水面。建筑用地包括居民点及工矿用地、交通用地和水利设施用地。未利用地指农用地和建筑用地以外的土地,包括滩涂、荒漠、戈壁、冰川和石山等。
耕地面积 指经过开垦用以种植农作物并经常进行耕耘的土地面积。包括种有作物的土地面积、休闲地、新开荒地和抛荒未满三年的土地面积。
林业用地面积 指生长乔木、竹类、灌木、沿海红树林等林木的土地面积,包括有林地、灌木林、疏林地、未成林造林地、迹地、苗圃等。
草地面积 指牧区和农区用于放牧牲畜或割草,植被盖度在5% 以上的草原、草坡、草山等面积。包括天然的和人工种植或改良的草地面积。
森林资源 指森林、林木、林地以及依托森林、林木、林地生存的野生动物、植物和微生物。林木指树木和竹子。森林指以乔木为主体的植物群落,是集生的乔木及与共同作用的植物、动物、微生物和土壤、气候等的总体。
活立木总蓄积量 指一定范围内土地上全部树木蓄积的总量,包括森林蓄积、疏林蓄积、散生木蓄积和四旁树蓄积。
森林覆盖率 指一个国家或地区森林面积占土地总面积的百分比。森林覆盖率是反映森林资源的丰富程度和生态平衡状况的重要指标。在计算森林覆盖率时,森林面积包括郁闭度0.2 以上的乔木林地面积和竹林地面积,国家特别规定的灌木林地面积、农田林网以及四旁(村旁、路旁、水旁、宅旁)林木的覆盖面积。计算公式为:

森林面积 指由乔木树种构成,郁闭度0.2以上(含0.2)的林地或冠幅宽度10 米以上的林带的面积,即有林地面积。森林面积包括天然起源和人工起源的针叶林面积、阔叶林面积、针阔混交林面积和竹林面积,不包括灌木林地面积和疏林地面积。
森林蓄积量 指一定森林面积上存在着的林木树干部分的总材积。它是反映一个国家或地区森林资源总规模和水平的基本指标之一,也是反映森林资源的丰富程度、衡量森林生态环境优劣的重要依据。
水资源 水在自然界中以固体、液体和气态三种聚集状态存在,分布于海洋、陆地(包括土壤)以及大气之中,通过水循环形成水资源。水资源包括经人类控制并直接可供灌溉、发电、给水、航运、养殖等用途的地表水和地下水,以及江河、湖泊、井、泉、潮汐、港湾和养殖水域等。水资源是发展国民经济不可缺少的重要自然资源。
矿产资源 矿产资源指由地质作用形成的,具有利用价值的,呈固态、液态、气态的自然资源,是社会发展的重要物质基础。
矿产基础储量 基础储量是查明矿产资源的一部分。它能满足现行采矿和生产所需的指标要求,是控制的、探明的并通过可行性或预可行性研究认为属于经济的、边界经济的部分,用未扣除设计、采矿损失的数量表表示。
矿产保有资源储量 指查明的矿产资源储量(资源储量=基础储量+资源量)扣除已开采部分损失量和加减应勘查,重算或其它原因增减量而得出的年底实有资源储量。
Explanatory Notes on Main Statistical Indicators
Total Energy Production refers to the total production of primary energy by all energy producing enterprises in the country (region) in a given period of time. It is a comprehensive indicator of the capacity, scale, composition and development speed of energy production of the country (region). The production of primary energy includes that of coal, crude oil, natural gas, hydropower and electricity generated by nuclear energy and other means such as wind power and geothermal power. However, it excludes the production of fuel of low calorific value, bioenergy, solar energy and secondary energy converted from primary energy.
Total Domestic Energy Consumption refers to the total consumption of energy of various kinds by production sectors and households in the country (region) in a given period of time. It is a comprehensive indicator of the scale, composition and development speed of energy consumption. The total energy consumption includes that of coal, crude oil and their products, natural gas and electricity, but excludes the consumption of fuel of low calorific value, bioenergy and solar energy. Total domestic energy consumption can be divided into three parts: (1) Final Energy Consumption: This refers to the total energy consumption by production sectors and households in the country (region) in a given period of time, excluding primary energy consumption and loss in the process of conversion into secondary energy. (2)Loss During the Process of Energy Conversion: This refers to the total input of various kinds of energy for conversion minus the total output of various kinds of energy in the country (region) in a given period of time. It is an indicator of the loss that occurs during the process of energy conversion. (3)Loss: This refers to the total loss of energy during the course of energy transmission, distribution and storage and the loss caused by any objective reason in a given period of time, excluding the loss of various kinds of gas due to gas discharges and stocktaking.
Elasticity Ratio of Energy Production is an indicator of the relationship between the growth rate of energy production and the growth rate of the national economy. The formula is:
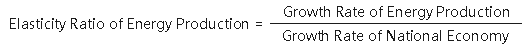
The average annual growth rate of the national economy can be shown by the gross national product, gross domestic product and other indicators, depending on the purposes or needs. The gross domestic product is used in the calculation of the ratio in this chapter.
Elasticity Ratio of Electricity Production is an indicator of the relationship between the growth rate of electricity production and the growth rate of the national economy. Generally speaking, the growth rate of electricity production should be higher than that of the national economy; in other words, electricity production should develop in advance of the national economy. Its formula is:
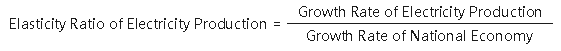
Elasticity Ratio of Energy Consumption is an indicator of the relationship between the growth rate of energy consumption and the growth rate of the national economy. The formula is:
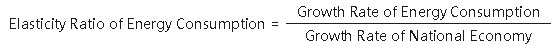
Elasticity Ratio of Electricity Consumption is an indicator of the relationship between the growth rate of electricity consumption and the growth rate of the national economy. The formula is:
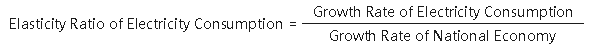
Efficiency of Energy Processing and Conversion refers to the ratio of the total output of energy products of various kinds after processing and conversion to the total input of energy of various kinds for processing and conversion in the same reference period. It is an important indicator of the current conditions of energy processing and conversion equipment, production technique and management. The formula is:

Land Resource Land refers to the surface of the earth,consisting of mainly rocks and its weathering and earth.Land resource can be classified,by its utilization,as land for agriculture,land for construction and unused land.Land for agriculture includes cultivated land,plantation,forestland,grassland and waters.Land for construction includes land for residential purpose,for manufacturing and mining,for transportation and for water conservancy projects.Unused land refers to land other than land for agriculture and construction,including beaches,deserts,Gobi,glaciers and rock mountains.
Area of Cultivated Land refers to area of land reclaimed for the regular cultivation of various farm crops,including crop-cover land, fallow,newly reclaimed land and land laid idle for less than 3 years.
Area of Afforested Land refers to land for trees, bamboos,bushes and mangrove including forest-cover land,bush-covered land,sparse forest land,land planned for forestation, slash and nurseries of young trees.
Area of Grassland refers to areas of grassland,grass-slopes and grass-covered hills with a vegetation-covering rate of over 5% that are used for animal husbandry or harvesting of grass.It includes natural,cultivated and improved grassland areas.
Forest Resource refers to forests,trees,forestland and wild animals,plants and microorganism that live on forests and trees. Trees include trees and bamboos.Forest refers to the population of clusters of trees and other plants,animals and microorganism as well as the earth and climate that have interactions with the trees.
Total Standing Stock Volume refers to the total stock volume of trees growing in land,including trees in forests,tress in sparse forests,scattered trees and trees planted by the side of villages,farm houses and along roads and rivers.
Forest Coverage Rate refers to the ratio of area of afforested land to total land area.It is a very important indicator that reflects the status of abundance of forest resource and ecosystem balance.Forest area includes the area of trees and bamboo growing with a canopy density above 0.2,the area of shrubby trees according to regulations of the government,the area of forest land inside farm land and the area of trees planted by the side of villages,farm houses and along roads and rivers.The formula for calculating forest coverage rate is as follows:

Forest Area refers to wooded area, i.e. the area of forest where trees and bamboo grow with a canopy density above 0.2 (inclusive) or a crown width above 10 meters,including natural and planted coniferous forest, broad-leaved forest,mixed forest, and bamboo groves, but excluding shrubbery and open forest.
Stock Volume of Forest refers to total stock volume of wood growing in forest area,which shows the total size and level of forest resources of a country or a region. It is also an important indicator of the richness of forest resource and the status of forest ecological environment.
Water Resource Water exists in the nature in solid,liquid and gaseous states, is distributed in the ocean,land(including earth)and air,and constitutes water resource through circulation.Water resource includes surface water and underground water that is controlled by human beings for irrigation,power-generation,water supply,navigation and cultivation.It also includes rivers,lakes,wells,springs,tides,gulfs and water area for cultivation.Water resource as an indispensable natural resource for the development of national economy.
Mineral Resources refer to useful natural resources enriched due to geological processes, in the form of solid, liquid or gas.Minerals are important material basis for social development.
Basic Reserves of Mineral Resources Basic reserves are part of total identified mineral resources that meet present mining and production standards,which is the part of reserve controlled, proven, and found to be of economic or marginal value through feasibility assessment or pre-feasibility study. Basic reserves are indicated as a figure including designing and mining loss.
Ensured Reserves of Mineral Resources refer to the actual reserves of mineral resources at the year-end, calculated as the proven reserves of mineral resources (Reserves of Mineral Resources = Basic Reserves + Resource) minus losses in previous extraction processes, plus or minus increases or losses due to exploration, recalculation or other reasons.



